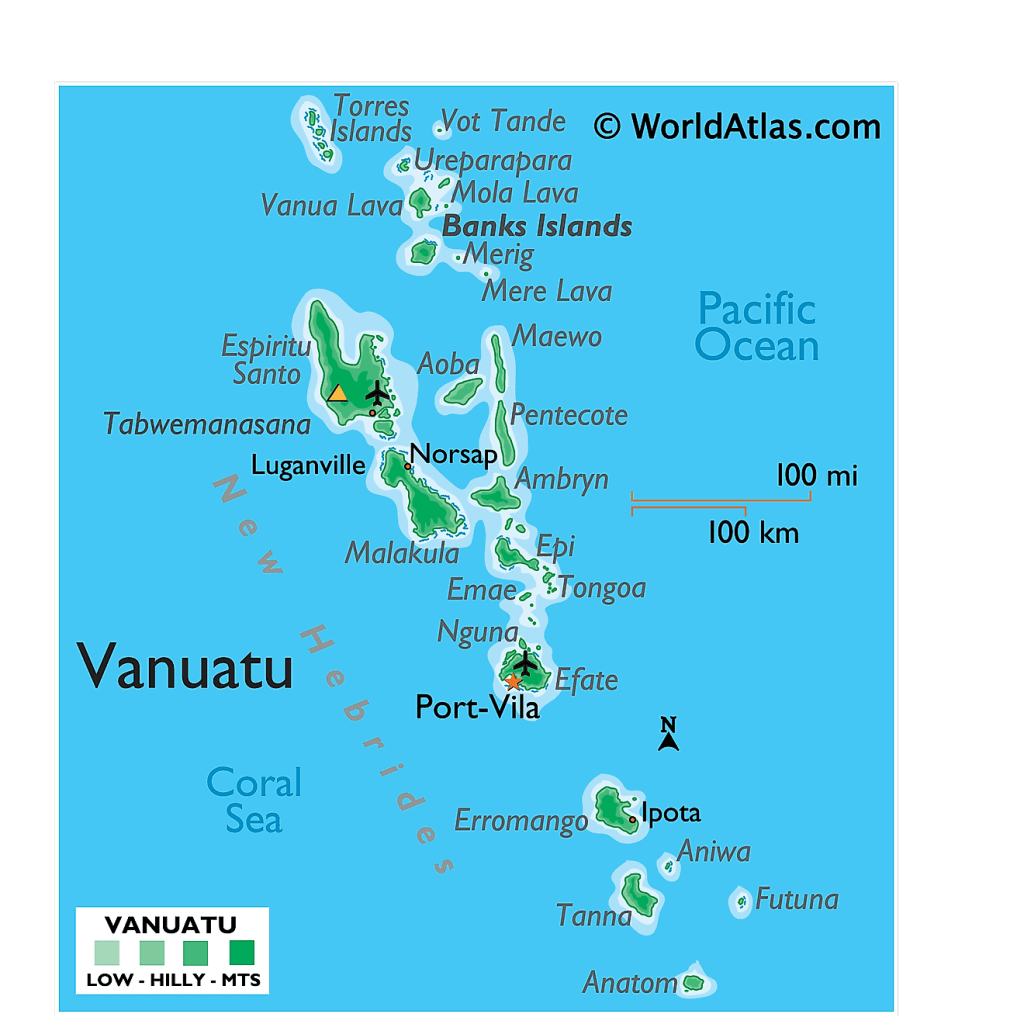
Vanuatu, formally known as the Republic of Vanuatu, is a sovereign island nation located in the South Pacific Ocean, comprising a diverse archipelago of 83 islands, including 13 principal larger islands and around 70 smaller islands. Covering a land area of 12,189 sq. km (4,706 sq. mi), Vanuatu lies geographically in both the Southern and Eastern hemispheres. It is situated to the east of Northern Australia, northeast of New Caledonia, west of Fiji, and south of the Solomon Islands.
The geography of Vanuatu is characterized by its rugged mountains and volcanic origins, with landscapes that include lush rainforests and active volcanoes. The highest point in Vanuatu is Tabwémasana, located on Espiritu Santo, the largest island, reaching an elevation of 6,165 ft (1,879 m). Most islands are surrounded by offshore coral reefs that contribute to their natural beauty and biodiversity.
Vanuatu is administratively divided into six provinces: Malampa, Penama, Sanma, Shefa, Tafea, and Torba, which are further segmented into municipalities. The capital and largest city, Port Vila, is located on the southern coast of Efate Island, serving as the nation’s commercial, administrative, and economic hub. This vibrant city is also a major port, facilitating trade and tourism.
The nation is home to a population of approximately 299,882 people. The currency used is the Vatu (VUV), and the country’s GDP stands at approximately $917.06 million, with a GDP per capita of about $3,058.07.
Overall, Vanuatu is known not only for its stunning natural landscapes and cultural richness but also for its strategic location in the Pacific, which has made it an important site for trade and tourism within the region. Its unique combination of geography, culture, and economy defines Vanuatu as a notable destination in the Pacific Islands.
Source link